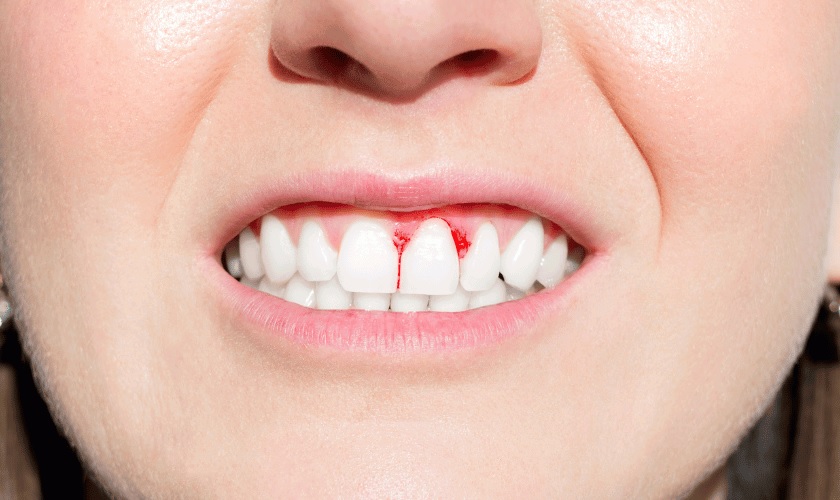
Periodontal disease is the most common persistent oral problem disorder that has tormented humans for decades. It is considered to be the leading cause of tooth loss if left untreated.
The Tukwila dentist and their team are committed to providing quality dental care for periodontal disease, thereby improving your overall health and well-being.
A comprehensive guide to periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, popularly known as gum disease, refers to a progressive infection and inflammation of the periodontium. The periodontium consists of the momentum, gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. Failure to treat the condition can cause the infection to spread from the gums to the bone.
Types
- Gingivitis: Involving swelling and reddening of the soft tissues (gums), which is usually reversible if treated on time.
- Periodontitis: This involves erosion of the gum tissues followed by bone deterioration and tooth mobility.
Causes
Bacteria is the most common etiological factor that, when left untreated, can lead to the formation of plaque that adheres to the tooth surfaces. This paves the way for increased bacterial infiltration that eventually hardens to form calculus. This releases harmful toxins and acids that erode the gums and destroy the underlying jawbone.
Risk factors
- Genetic predisposition
- Poor oral hygiene
- Pregnancy and menopause due to hormonal changes
- Smoking
- Stress
- Medications such as immunosuppressants and those that reduce saliva production
- Certain autoimmune diseases like lupus
- Heart or respiratory disease
Warning signs
Some of the common and obvious signs of periodontal disease include:
- Red, swollen gums
- Tender, painful gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Pain when chewing
- Poor bite due to malocclusion
- Receding gums
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Loose teeth
A detailed explanation of treatment options for periodontal disease
Treatment options include:
Non-surgical options: For mild to moderate cases
- Professional oral cleaning
- Supragingival cleaning
- Deep subgingival scaling
- Root planing
- Medications
- Antibiotic gels
- Antimicrobial mouth rinse
- Enzyme suppressants
- Gingival pocket irrigation
Surgical options: For moderate to severe cases
- Flap surgery
- A flap surgery helps reduce the size of the gingival pocket between the gums and the teeth.
- Tissue regeneration
- A biocompatible membrane is inserted into the affected area to promote regeneration of the tissues.
- Gum grafting
- Helps to reattach the lost gingival tissues on the exposed tooth surface
- Bone grafting
- Aids in bone regrowth using graft material.
- Dental implants
- Replace lost teeth by inserting screw-like posts that mimic your lost tooth roots to provide anchorage to permanent restorations like crowns and dentures.
Summary
Periodontal disease can be debilitating if not treated on time. Knowing the warning signs paves the way for early diagnosis and treatment to improve your oral health and integrity.